Newton Orchards现在能够直接与最终消费者联系,推出一项营销活动,提高Newton Orchards品牌的知名度,并利用DiMuto的智能营销服务向澳大利亚的消费者传达从农场到餐桌的追溯故事。
DiMuto基于QR码的智能营销服务是一种经济高效的解决方案,可以接触到最终消费者,并传达农民和生产者的追溯品牌故事。
关于Newton Orchards:Newton Orchards位于西澳大利亚州的Manjimup,是一个经营超过90年、有四代人的家族企业。多年来,它发展成为澳大利亚最值得信赖的水果种植者之一。
- 拥有水果衍生饮料系列,包括苹果酒和果汁,以减少食物浪费
- 种植各种作物,如苹果、梨和樱桃
- 向Coles和Woolworths等主要零售超市供应新鲜农产品
- 行业:新鲜农产品
- 位置:西澳大利亚州Manjimup
DiMuto的成果
- DiMuto数字资产创建(DAC)和交易平台提供了贸易追溯性,有助于提供完整的供应链可见性
- 智能营销解决方案帮助吸引最终消费者,加强Newton Orchards品牌
主要挑战
- 无法直接接触最终消费者并了解他们的客户
- 无法满足消费者对新鲜农产品追溯性的需求
- 难以为其新鲜农产品和饮料产品进行交叉促销
- 难以将Newton Orchards苹果与市场上其他现有品牌区分开来
对于许多种植者和生产者来说,往往很难将他们的产品与市场上的现有产品和品牌区分开来。这使得进入新市场或销售渠道变得具有挑战性。此外,作为食品供应链的上游参与者,他们通常依靠中间商将产品交付给最终消费者,因此无法直接与消费者沟通。与此同时,越来越多的消费者在购买新鲜农产品时要求追溯性,因为他们希望确保所购买的农产品经过安全处理并具有良好的质量。尽管农民一直遵守安全法规和良好的加工实践,但很难将这一点传达给最终消费者。
DiMuto如何帮助
DiMuto的SMART营销解决方案为农民与最终消费者之间建立了简单的连接。作为DiMuto贸易解决方案平台的一部分,销售与市场保留与认知工具(SMART)营销解决方案允许像Newton Orchards这样的新鲜农产品种植者和供应商进行成本效益的营销活动,以吸引消费者的参与。
通过DiMuto的SMART营销,Newton Orchards能够利用贴在每个苹果上的DiMuto QR标签与最终消费者进行沟通。当消费者扫描QR码时,他们现在有能力了解一个简单苹果背后的历程,并了解苹果的产地、种植实践以及这个四代农场的历史。
Newton Orchards现在还能够通过DiMuto的SMART营销进行直接营销活动。他们在西澳大利亚市场举办了一次幸运抽奖活动,旨在提高人们对其苹果汁和苹果酒的认知,以及对新鲜的粉红女士苹果的追溯性故事。
这次营销活动在现场消费者中获得了积极的反馈,通过销售点的品尝和营销活动,显示出消费者对追溯性和QR营销的积极响应。幸运抽奖机制还使Newton Orchards能够了解他们最终消费者的行为和偏好,并与他们建立起关系。
为了利用DiMuto的SMART营销,Newton Orchards采用了DiMuto的追溯解决方案,以捕获他们的供应链信息,包括DiMuto QR标签。这使他们能够向最终消费者传达可验证的追溯故事,并将追溯性作为区别于其他品牌的工具。
“作为向澳大利亚消费者提供可持续和安全食品的承诺的一部分,我们很高兴与DiMuto合作。通过能够追踪每个苹果的从农场到餐桌的过程,我们能够确保食品的完整性,让顾客以更接近自然的方式享受苹果,” Newton Orchards的业主兼经理Harvey Giblett表示。通过经过DiMuto验证的产品和贸易,Newton Orchards现在能够利用追溯性来区分他们的品牌,并加强他们向最终消费者传达农场到餐桌品牌的能力。
如果您对了解DiMuto如何帮助新鲜农产品种植者通过追溯性来提升品牌感兴趣,请在此处与我们联系,或发送电子邮件至[email protected]。
区块链、人工智能和物联网如何简化农业食品产品质量,实现更高效、可持续和透明的食品供应链。
在当今社会,农业食品贸易实践已经发展,以满足消费者对高质量、安全和可持续食品产品的需求。帮助农业食品企业满足这一需求的关键工具之一就是区块链。
区块链技术的使用已成为确保农业食品贸易交易高效和透明的重要工具。此外,对食品来源的了解在最终消费者中变得越来越普遍,这使得农业食品企业更有必要更好地了解、管理和沟通产品从农场到餐桌的流动情况。
区块链技术是什么?
区块链是一种共享的分布式账本技术,允许用户彼此共享经过验证、不可篡改的信息。通过这种方式,区块链帮助农业食品供应链各方共享可信信息,用于每笔交易,从而实现食品来源的追踪,建立更加可见、高效和透明的供应链。
区块链可以用于诸如改善农业食品供应链中的食品质量控制等应用。
利用区块链、人工智能和物联网来改进产品质量控制
研究表明,由于不适当的储存和运输条件,水果和蔬菜被丢弃。例如,在中亚和南亚地区,运输损失可能高达整体产量的30%,造成大量浪费。
随着农业食品产品沿着食品供应链进行运输,它们通常会选择不同的路线,并经历许多处理环节。这意味着在整个供应链中跟踪农产品是具有挑战性的,这使得确保产品优质成为一项困难任务。在保鲜产品行业尤其如此,因为确保质量是最大化货架寿命的关键。
农业食品企业需要克服以下问题,以确保产品质量:
- 处理大量的贸易、产品和文档信息。
- 没有充分利用有价值的技术。
- 跟踪产品信息。
- 优化确保产品质量信息的过程。
DiMuto如何运用区块链、人工智能和物联网确保产品质量
DiMuto利用区块链技术结合物联网(IoT)和人工智能(AI)以客观简化的方式来确定产品质量。
DiMuto通过以下四个步骤改变了确保产品质量的方式:
- 1. 利用我们的数字资产创建(DACKY)设备中的物联网技术,捕捉整个供应链中每个单独箱子的产品数据。
- 2. 将收集到的数据整理并在我们的贸易解决方案平台上,使其对不同用户可访问、可读、易懂。
- 3. 使用人工智能为收集到的数据提供更多洞察力。
- 4. 数据被保存在区块链上,以确保其不可篡改性。
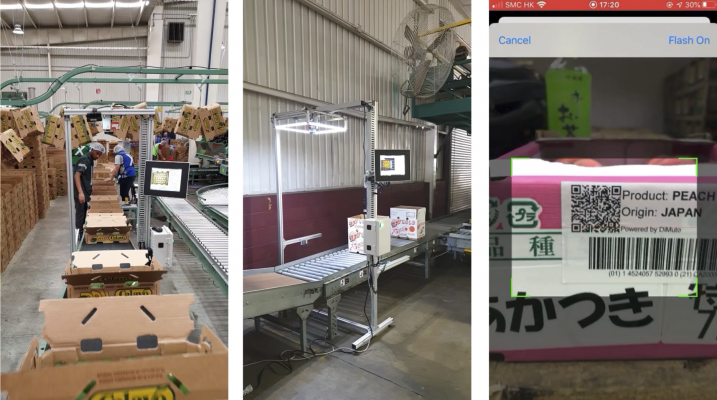

DiMuto的DACKY设备在各个包装设施捕捉预装运箱的信息。

每个农业食品产品的包装箱的视觉图像随后会自动上传到DiMuto平台,并与每笔交易关联,以便农业食品组织中的产品、质量控制和销售团队可以轻松地访问这些数据。
DiMuto的人工智能和机器学习技术会增强所收集的信息,利用预测模型和分析提供有用的洞察力,这个过程会获得重要的产品信息,以评估其质量得分:
- 产品识别
- 产品尺寸
- 产品数量
- 产品质量
请观看上面的视频,了解DiMuto如何利用人工智能来确定预装和后装运产品的质量。
这些有见地的数据将存储在区块链上,通过分散的节点网络确保安全性和不可篡改性。
在当前将重要信息保存在中央服务器的做法中,存在单点故障的风险。然而,在区块链中,数据分布在网络中的所有节点之间。因此,它防止了系统受到中央机构的控制。因此,产品质量信息的获取方式始终简单且安全。
这将有助于更高效地确定农业食品产品的质量,帮助农业食品企业在供应链的各个阶段更好地控制食品质量。
通过DiMuto的解决方案,农业食品公司可以减少由于供应链中更加可见、高效和可靠的产品质量控制而引起的食物浪费,并迈向食品可持续发展的下一步。
如果您对了解更多有关DiMuto如何帮助农业食品公司利用区块链和其他技术来建立更高效、可持续的供应链感兴趣,请在此处与我们联系,或发送电子邮件至[email protected]。
Pandemics are characterized by their severe negative consequences on the global economy. COVID-19 has had a significant influence on one of the most vital areas of the economy – the whole food supply chain, from the source to the consumer. The disruption to supply networks continues to be severe, with the virus continuing to cause numerous areas and economies impose lockdowns and restrictions, while others struggle to adapt to a post-pandemic landscape. The supply chain will be crucial in providing products and services promptly, reliably, and securely as economies begin to recover.
COVID-19 is causing the ‘Messy Middle’ in operations to be more challenging throughout the world in ways that are difficult to predict and measure. Agri-Food businesses are concerned that they will not be able to meet contractual commitments on time due to the new challenges posed by the pandemic and the lack of visibility; from Supplier to Retailer to End-Consumer. There remain substantial concerns regarding food production, processing, distribution, and demand in lieu of pandemic-related supply chain changes such as limitations to workers’ mobility, changes in consumer demand, the closure of food production facilities, new food trade laws, and financial constraints in the food supply chain.
In addition to the new obstacles posed by the pandemic, COVID-19 revealed previously unknown weaknesses in several sectors – Lead Times, Lack of Diversification and Visibility, and many organizations have experienced heavy losses because of it, exacerbating and hastening issues of the ‘Messy Middle’ that previously existed in the supply chain.
How The Pandemic Impacts the Global AgriFood Supply Chain
From farm to fork, there are five phases of the food supply chain (FSC). Two mechanisms are used in the food supply chain for food consistency and protection. The first focuses on rules and legislation that use mandatory requirements reviewed by government agencies. The second focuses on voluntary principles established by economic law or international organizations. FSC contains important final stages that can easily affect end-consumers. This includes safe food handling, preparation, delivery, the use of personal protective equipment such as helmets and gloves, surface disinfection, and work. Maintaining environmental and even social distance are some safety measures implemented to ensure the continuity of food flow.
The Covid-19 pandemic, unlike foot-and-mouth disease, avian influenza, and Listeria, does not directly infect animals or produce and therefore has no impact on development of diseases via produce. However, because of the pandemic, nations have severely restricted the flow of goods (land, sea and air transport) and the movement of labour around the world to manage and control the rate of transmission of Covid-19 between people.
Reportedly, Australia’s isolation rules have also created shortages of workers to harvest, pack, transport and distribute the fruit and vegetables which leads to strained distribution of food supplies. These conditions are aggravated with Uganda’s authorities demanding fresh testing of Covid-19 by the Kenyan truck drivers upon their arrival at the border with claims that their Covid-19 certificates are falsified, enabling the Truck Drivers to go on a strike due to the stated conditions. These situations greatly delayed the supply of fresh produce.
Chile Scrambles to Regain China’s Confidence on Cherry Imports
Chile’s association of fruit exporters Asoex stated that wholesale purchases of Chilean cherries have decreased to 4% below normal levels in 2021 and retail sales flopped heavily by 63% in China.
The cause of reduction for cherry imports in China is due to reports that have been made stating that some imported cherries tested positive for traces of the coronavirus in Jiangsu Province, which swiftly spread across the Chinese media making the consumers doubt and lose confidence in purchasing them. This incident impacted the cherry sales negatively as cherry sales suffer a devastating blow due to the fear of being contracted with the Covid-19 virus.
COVID-Driven High Freight Rates Makes Receiving Poor Quality Fresh Produce More Costly
According to the Xeneta Shipping Index, there has been an increase in freight rates, with global container prices rising by 3.2% in September 2021, which marks an astounding surge of 91.5% as compared to the previous year. As the costs are high in shipping fresh produce, receiving poor quality fresh produce would further incur loss in sales where a container of Fresh Produce can value between US$50,000 to US$150,000 and wasted costs that are not easily recovered where rises in freight costs are at an all-time high making goods rejection even more costly.
How DiMuto Helps AgriFood Companies Stay Resilient
DiMuto understands the many difficulties in conducting cross-border international agrifood trade, and the various risks involved, due to the disconnected flow of information across global supply chains where buyers and suppliers are often located in very distant geographical areas.
With DiMuto and our trusted network of buyers in the region, you can trade Agri-Food products and fresh produce products with seamless visibility and accessibility. DiMuto’s Global Trade Network is made up of an exclusive network of trusted buyers and suppliers conducting traceable trade on the DiMuto Platform. With full supply chain visibility, growers and retailers can buy & sell fresh produce more effectively and efficiently.
For Buyers:
When retail stores receive goods that do not fulfil order specifications or products that have some form of quality issues. Moreover, the defects are only known when the fruit or produce has arrived due to a lack of product visibility along the supply chain. This makes trade managing fresh produce challenging for retailers:
- Unable to see pre-shipment product quality and container loading
- Unable to quickly respond to inventory changes due to rejections from quality defects
- Unable to communicate defects easily and effectively between internal teams
With DiMuto, Retailers can now enjoy accessible visibility of pre-shipment and post-shipment quality to better manage any potential loss of sales
- Pre-shipment product quality down to every single carton easily accessible to commercial team
- Trade information, documents and actions of each trade seamlessly recorded and presented in timeline view
- Post-shipment product quality efficiently captured and communicated between QC, commercial and retail teams
- Dashboard view of Inspection Management to ensure optimal product quality and vendor performance
Read more on How Retailers Can Better Manage the Impact of the ‘Messy Riddle’
For Suppliers:
By joining DiMuto’s Global Trade Network, you will deal with traceable, trackable fresh produce that has been digitized TradeTrust Blockchain Validation, creating data-backed trust and peace of mind when you conduct global produce trade adapting to the pandemic that has disrupted trade.
Read more on How DiMuto Uses TradeTrust Blockchain Validation to Strengthen Trust in Global Trade
Pukuna Farms Using DiMuto’s Traceability for Visiblity and Accessing New Markets
Based on a challenge faced by one of our customers – Pukuna Farms, they were finding a way to expand their market to such an unknown region like Asia, hailing all the way from Ecuador. It is not easy to enter an unknown market and for that, the supplier has to be reliable, where consistent quality is key. Buyers need to be assured that suppliers will sell their fresh produce in good condition and they will be receiving the products as per specified and upon the arrival of the fresh produce and buyers will be required to scan the fruits for visibility on the quality of fruits. For that, it is important to have full visibility in the supply chain.
With DiMuto’s traceability solutions, traceability and digitalization secured with Blockchain-Powered solution, Pukuna Farms was able to improve in sales as each Pitahaya is digitalized with DiMuto QR code so it can be tracked and traced on one single platform to provide full visibility as it moves through the supply chain, making it easier to manage trade dispute based on the information recorded timely on the DiMuto platform.
Product quality, farm information and trade information are captured on the DiMuto platform. Thus, the visibility provided by DiMuto to supply chain partners enables trade traceability and transparency, improving trust and establishing long lasting partnerships between supply chain partners.
Read more on how Pukuna Farms Uses DiMuto’s Traceability.
DiMuto Creates Trade Visibility for “The Messy Middle”

DiMuto’s Accessibility of Pre-Shipment and Post-Shipment Quality
With DiMuto, Retailers can now enjoy accessible visibility of pre-shipment and post-shipment quality to better manage any potential loss of sales
- Pre-shipment product quality down to every single carton easily accessible to commercial team
- Trade information, documents and actions of each trade seamlessly recorded and presented in timeline view
- Post-shipment product quality efficiently captured and communicated between QC, commercial and retail teams
- Dashboard view of Inspection Management to ensure optimal product quality and vendor performance
Fundamental shifts in consumer behaviour, supply networks, and routes to market have made Agri-Food companies face challenges in adapting and resolving them. As a result of the pandemic, companies must expedite the implementation of efficient solutions to navigate the unpredictability.
If you are interested to learn more about how DiMuto helps Agri-Food businesses leverage on an increased visibility to stay resilient amidst the challenges of the pandemic in the supply chain, please reach us here or drop us an email at [email protected].
Entering into the New Era of Smarter Food Safety in 2022 – Food Traceability is an emerging need in today’s world with open global markets and is a step towards making end-consumers become more aware of the food they consume and setting up sustainable and ethical food supply chains.
Food Traceability means being able to know the origin and traces of food products along the stages of the food supply chain – production, processing, manufacturing, distribution and consumption, ensuring visibility and transparency throughout the different stages of the supply chain.
Securing visibility and transparency within the whole food supply chain, traceability for movements of fresh produce will require robust technical solutions such as blockchain technology which enhances the ability to quickly pinpoint potential sources of contamination to efficiently prevent, contain or rectify outbreaks.
Food Traceability Will Lower Implementation Costs And Become a Norm
In The AgriFood Industry

Blockchained Durians
Transparency in terms of blockchain food traceability can validate and authenticate the provenance of food and improve the brand’s credibility. Therefore the use of blockchain technology has become an essential tool to ensure efficiency and transparency for AgriFood trade transactions. Additionally, understanding food provenance is becoming more prevalent among end-consumers, making it critical for AgriFood businesses to better understand, manage and communicate product movement from farm to fork.
There Will Be A Strong Growth In Food Traceability Industry On A Global Scale
Between 2000 and 2016, world agricultural trade increased more than threefold in value, rising to USD 1.6 trillion in 2016. Market revenue growth is expected to be driven by rising demand for food traceability systems to identify necessary documentation and tracking for each stage of food processing. Increase in demand for important tools in the agri-food sector represents a very useful tool for analysing, monitoring and managing the flow of products.
Food Safety Concerns And Growing Eco-Consciousness Will Continue Influence Consumer Purchase Decisions
Food safety concerns have become critical in many countries, especially those with lack of standards, regulations, and stringent stipulations governing quality and safety of food and edible products.
Post COVID-19 pandemic, a sizable number of consumers developed some level of fear related to what they eat and who has been in contact with what they consume. This has been playing a major role in a number of companies deploying additional safety measures in order to support brand value, increase consumer trust, and drive revenues. This in turn has been adding a significant boost to demand across certain supply chains that have deployed the right measures and have built trust and enabled better traceability of food products.
With longer and more complex supply chains giving rise to the “Messy Middle”, tracking from farm to fork requires increased scrutiny and accountability throughout the process.
How DiMuto Helps
DiMuto Trade Management Solutions provide an all-in-one platform to help AgriFood companies track physical AgriFood products for each trade, down to each carton and product. Using our unique Digital Identities Labels (DIDs), companies can digitalize physical products and combine it with the relevant supply chain data on our blockchain-powered platform. Such traceability information can be shared efficiently within departments of the same organization, as well as with external stakeholders such as buyers, retailers and end consumers. This can be done by scanning each carton to access a web-based Product Passport, for consumers, or achieved through our “Quick Info” function for trade partners. By making the sharing of verified traceability data, AgriFood companies can now better manage food safety requirements in cross-border supply chains.

If you are interested to learn more about DiMuto’s Trade Management Solutions can help you achieve Food Traceability, talk to our sales team today at [email protected].
Cross-border Transactions Today
In 2020, the market growth for international payments reached an all-time high with forecasted revenues of $2Trillion USD, according to a recent forecast by Smarter Payments Tracker. However, research has shown that only 1% of small and medium enterprises (SMEs) use digital finance successfully, even though SMEs represent and more than 50% of employment worldwide.
Add that to the complex regulations and infrastructure of cross-border payment systems today, it is no wonder that moving money across borders is still far from an efficient and easy process. This problem will only become more pertinent as the role of SMEs in the global economy continues to grow. Challenges faced when conducting cross-border payments include:
- Country-specific regulations
- Slow processing of transactions
- Expensive costs
- Security concerns
- Lack of visibility
Country-specific rules have impeded international payments, and transactions routed through intermediate institutions can take days to complete and typically come with costs. Due to the numerous intermediaries involved in transferring money from one nation to another, all of which collect fees for their services, cross-border payments are notoriously expensive. Regulatory costs pile up, and FX fees for converting one currency to another will be levied. Compounding this is the lack of clarity when it comes to remittance fee structures.
Additionally, unlike near-instantaneous domestic payments, traditional cross-border bank transfers typically involve numerous exchanges of hands in one transaction and take two to five days to process, making it difficult to expect payments on time.
On top of that, high-level security breaches in cross-border payment systems are common, as evidenced by the $81 Million theft on Bangladesh’s central bank in 2016. As each country has its own set of rules, the cross-border payment system is vulnerable to hacking whenever funds enter a country with lax security and access policies.
As each country has its own set of rules, the cross-border payment system is vulnerable to hacking whenever funds enter a country with lax security and access policies.
Another core concern of businesses making cross-border payments is the lack of visibility of payment status. according to a poll conducted by SWIFT and EuroFinance in 2017, 64 percent of businesses desire real-time payment tracking capabilities, while 47 percent want improved insight into the costs and deductions involved.
With the longstanding lack of real-time tracking of payment status, businesses often do not have certainty of transaction status. When companies need to know the current status of a payment, they are dependent on operations specialists undertaking manual research to ascertain basic information. Payment inquiries must be directed through correspondent banks, then communicated back to clients to determine any necessary actions. This lack of transparency creates a high informational cost, undermines corporate cash flow forecasts, and can strain relationships with a client’s suppliers and busines partners when funds are not received as expected.
For AgriFood companies with a significant portion of business in export-import trade, the ability to conduct and manage payment transactions across borders in an efficient, secure and visible manner is a concern. The risks of cross-border payments today are especially great for AgriFood companies dealing with a high volume of international trade transactions where one container of fresh produce can easily amount to an average cost of USD$50,000 to 150,000.
A need for trade-centric payment management in global AgriFood Trade
In global AgriFood Trade, there’s not only a need for cross-border payment methods to have less friction but have a trade-centric perspective as well. This is because product movement is dependent on a multitude of factors and delays and changes in timelines are commonplace. Trade disputes involving quality issues are typical and can cause upwards of 5-15% of trade value.

Trade Dispute Due to Poor Product Quality of Oranges, read more.
Thus, it is particularly important for finance teams to be informed of situations affecting expected payments and cash flow.
DiMuto Unifies Products, Documents and Payments in One
DiMuto connects products, documents and payments on a single platform, giving visibility across departments and functions in a company. We digitalize physical AgriFood products by tagging each fruit or vegetable with a Digital Identity Label (DID).

DiMuto’s DIDs Tagged onto Cartons of Bananas to Provide Visibility Across All Departments, read more.
DIDs act as a digital identifier for each fruit and contain product quality and traceability data and allow companies to connect the product to digital documents and payments on DiMuto Platform.
DiMuto Payment Management
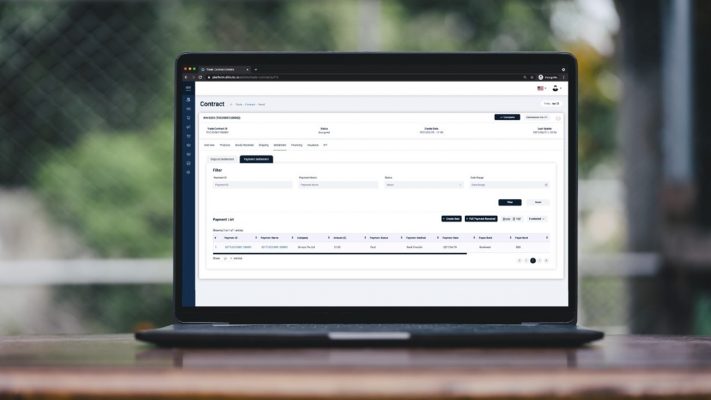
DiMuto allows payment receipts to be uploaded onto the blockchain automatically, ensuring immutability. Payment status is also viewed in the same trade timeline as other trade actions, ensuring that both sales and finance understand the trade situation. The DiMuto Payment Management feature also allows companies to conduct cross-border transactions via the DiMuto Platform.
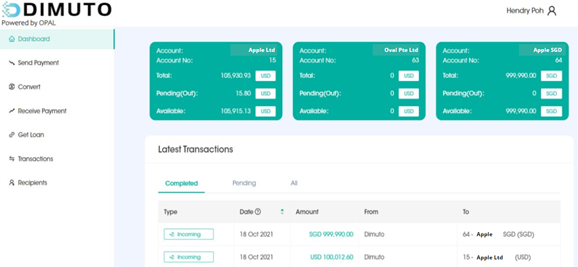
DiMuto Payment Powered by OPAL
A partner that we work with to make this possible is OPAL Payments, a Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS)-licensed Major Payment Institution (MPI), which provide businesses with a less expensive and more convenient method of international payment and cross-border banking through Global Digital Business Accounts.
Through this partnership, companies on the DiMuto Platform will be able to receive payments rapidly in important markets such as the United States, the United Kingdom, the European Union, and more, as well as access local payment networks in 21 countries without the need to set up business operations in these territories. OPAL understands that SMEs encounter challenges when it comes to transacting business on a global basis.
Beyond connecting payments in traditional currencies, the DiMuto Payment Management can allow transactions in the USD Coin (USDC), through CIRCLE, a uniform platform for businesses to collect payments and send payouts around the world using blockchain technology. Meeting the needs of high-volume trading firms, crypto exchanges, and market makers, the USD Coin (USDC) is a significant advancement in the way businesses utilize money. Digital dollars function similarly to other digital content: they travel at the speed of the internet, can be traded in the same manner that we share content, and are less expensive and more secure than current payment systems.
A Bright Future: Paving the way to trade financing access
By digitalizing physical AgriFood assets, asset tracking is now possible – the identity, movement and condition of individual products and cartons can now be easily tracked and traced with DiMuto. Coupled with Artificial Intelligence Models that can objectively assess product quality and trade health, DiMuto helps lower the risk associated with trade financing for agri-perishables, giving AgriFood SMEs opportunities to obtain much needed trade financing options.
The US$1.9 trillion global trade finance gap has deteriorated as a result of Covid-19, which is now projected to be as high as US$3.4 trillion by experts, with SMEs in emerging nations being the hardest hurt. Due to concerns such as creditworthiness, collateral requirements, short-term liquidity, and political or currency risk, SMEs have historically had difficulty obtaining institutional funding.
More efficient and trade-centric cross-border payment methods will not only create more visibility and help business manage their operations and cash flow better but also help to provide them with trade financing opportunities to help their businesses grow greater.
If you are interested to learn more about how DiMuto helps Agri-Food businesses with cross-border payment management, please reach us here or drop us an email at [email protected].
With growing demand for transparency and traceability of global food supply chains – the Food Traceability market is estimated to be worth as much as US$9.28billion by 2028, it is no wonder that there has been much data-driven innovation in the AgriFood sector. There has also been increasing recognition of the need for a digitalized food system, particularly in the wake of Covid.
However, critical digital and physical documentation required to conduct AgriFood trade continues to be disseminated, recorded and stored in an inefficient, disconnected and unsecure manner across the various stakeholders in the AgriFood supply chain.
Importance of Trusted Supply Chain Trade Documents in AgriFood Trade
Agriculture and food commerce are more complicated than manufacturing trade because trade standards are more stringent, documentation is more cumbersome, and logistics are more complicated – these are often necessary to ensure consumer food safety. For food safety, detailed information on traded items as well as the movement of goods in a supply chain is vital and these challenges have been exacerbated by the rise in e-commerce.
Thus, the need for trusted digital documents showing the food safety status and traceability data of food products is needed more than ever. For instance, in lieu of the pandemic, China has implemented strict policies on food imports and even banned imported fruits and salmon from specific ports. For AgriFood companies dealing with food import-exports, being able to efficiently and effectively store digital documents and trade information and ensure its validity and authenticity in crucial to ensure trust in the provenance of their food products.
How Can AgriFood Businesses Be Assured of the Security of Their Uploaded Documents?
Data breaches, document forgeries, and fraudulence have become a pressing issue for digital documents on the web or businesses’ private platforms. It is crucial to note that although there are several methods for digitizing documents and storing digital documents, the security and efficiency of such methods may not be as seamless and transparent as one might think.
Current communications occur over different communications platforms such as social messaging apps and emails, causing crucial trade information and documents to be scattered and stored inefficiently, making it challenging for AgriFood companies to ensure timely verification of these documents, or store and retrieve them securely.
How DiMuto Helps – DiMuto Creates Trade Visibility for “The Messy Middle”

With DiMuto, Retailers and Suppliers can now enjoy greater visibility of all their trade data. Product, document and payment data are all tracked on a single platform. Suppliers, Traders and Retailers are able to easily access all relevant trade documents which are automatically uploaded onto the blockchain, ensuring immutable records of the trade action and documents.
In addition to utilizing the blockchain to build trust, DiMuto utilizes Dedoco, a decentralized digital signing platform on blockchain, to further authenticate trade documents.
How DiMuto Authenticates Trade Documents on the Platform with Dedoco
AgriFood Trade documents on DiMuto are further authenticated with Dedoco’s blockchain-enabled electronic signature platform to increase the credibility of digital documents. Documents are readily signed using Dedoco and registered with a unique blockchain hash when they are published to the DiMuto platform. Documents’ signatures can also be verified Dedoco web.

Digital Documents will require signatures that are then embedded with a blockchain hash
With blockchain-verified signatures that act as a guarantee of document authencity, DiMuto ensures credibility of every trade transaction – removing barriers such as security risks, fraudulence, and forgery of documents. DiMuto’s All-in-One trade management platform helps strengthen trust and confidence among AgriFood players in the food supply chain.
If you are interested to learn more about how DiMuto ensures trust for global AgriFood trade transactions, talk to our sales team today at [email protected] and find out how DiMuto can support your journey to better trade visibility. www.dimuto.io
投资可持续食品系统的需求极为紧迫。预计到2050年,全球人口将增至98亿人,这将对我们现有的食品系统造成更大的压力。此外,气候变化的影响给农业带来了额外的威胁。气候变暖可能导致农作物产量下降超过25%,而与气候变化相关的极端天气事件可能对农民、土地和作物造成毁灭性影响。
谁是小农户?
小农户是在不到2公顷可耕地上种植商业作物或养殖的个人。小农户还可能在不同国家拥有多个土地持有,但其总土地持有量必须在2公顷以下。

小农户在可持续食品系统中的角色
在得到正确的支持下,小农户可以成为全球保护和再生自然的先锋。赋予小农户采用可持续和再生农业实践的能力,使他们能够为当前和未来的世代恢复土地,同时增加产量、增强农业韧性,为农民及其家人创造繁荣,并对环境产生积极影响。
以巴西为例,斯德哥尔摩环境研究所的一份报告发现,“2004年至2011年间,拥有500公顷(1235英亩)以上土地的地主负责了约48%的森林砍伐。同期小农户拥有的土地造成了12%的森林破坏。然而,自2005年以来,最大土地所有者对年度森林砍伐的贡献减少了63%,而小农户的贡献增加了69%。” 小农户的农场在确定是否能实现可持续的食品系统方面至关重要。
小农户面临的盈利挑战
很少有小农户能够获得正式培训、先进的农业用品和设备以及财务能力,以提高土壤健康和生产力。许多小农户还缺乏官方文件证明其财产所有权,限制了他们在种植何种作物、何时种植以及如何种植方面的选择。因此,长期可持续的农业实践很少得到优先考虑。
小农户还受到一些系统性问题的影响,比如性别不平等、健康问题和缺乏卫生设施。因此,在帮助小农户采用再生农业原则方面存在重大障碍和潜力。
此外,许多因素限制了小农户对城市消费者的贡献。因此,显而易见,一个可持续的食品系统必须得到政策支持,使小农户能够实现其全部潜力,同时处理外部性和限制。
如果小农户要在可持续食品系统中扮演重要角色,作为可持续食品生产者和食品安全提供者,他们需要得到培训、设备和融资,以奖励他们采用可持续的耕作实践。然后,挑战在于确保监测和确保真正可持续的农民得到帮助。
小农户如何从数据可见性中受益?
根据Emergen Research的数据,全球食品可追溯性市场规模在2020年达到45.4亿美元,并预计到2028年将达到97.5亿美元。
对于食品可追溯性系统的需求不断增长,以实现强制性文件工作和对食品加工每个阶段的跟踪,预计将推动这一收入增长。农食品部门对关键技术的需求增加,这是一种非常有用的工具,用于分析、监测和规范产品流程。通过数字化农场数据和可见性,小农户可以组织和改进农场,实现更高的利润率和可持续增长。
此外,随着对食品可追溯性技术的需求在对环保有意识的最终消费者和食品企业中都不断增加,对小农户在农田上行动的可见性将成为追踪食品产品来源的关键。
DiMuto如何帮助小农户实现可持续性和可见性?
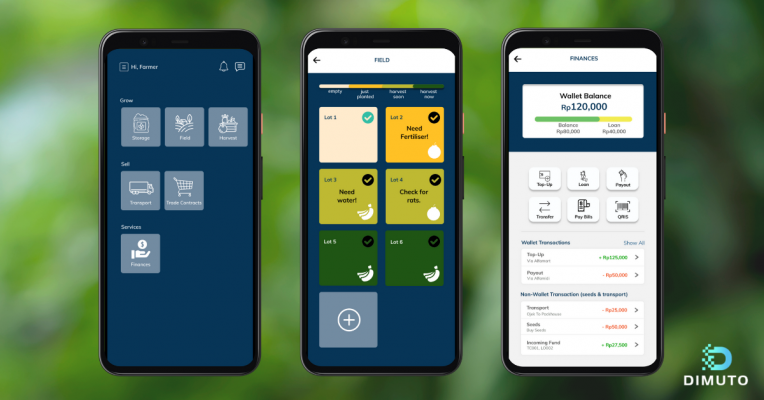
从左到右:农场概况、农场地块输入信息、农场钱包
DiMuto农场管理应用程序通过三个功能-种植、销售和服务,连接了种植、收获、销售和付款,以实现农场运营的更好可见性。使用DiMuto农场管理应用程序,小农户可以在几分钟内在农场管理移动应用程序上建立他们的数字身份,并与采购团队和农业专家等买家建立联系。通过直观的界面,农民可以简化农场管理,轻松存储和访问数字化的农场记录、运输和销售信息。此外,他们还可以获得产量估算,跟踪生产情况,并获得及时提醒来管理他们的田地。
通过DiMuto农场管理应用程序,小农户现在可以:
- 在一个地方简化农场管理,并随时随地跟踪所有与农场有关的记录。
- 连接种植、收获、销售和付款,以更好地了解农场运营情况。
- 借助可以追溯到农场的农产品,获得更好的价格、市场地位和高端买家。
- 获得更好的计划和产量估算可见性,跟踪生产情况,并识别趋势和潜在问题。
这些农场数据随后会自动填充到汇总的网络仪表板,供农业专家和采购团队跟踪农场和预估收成,为供应计划提供更准确的数据。农场管理还与DiMuto平台的生产管理和贸易管理功能无缝连接,使农食品公司能够追踪其农食品产品和原材料的来源,直至其产地农场和地块。作为验证的附加层,所有记录在DiMuto平台上的供应链数据也会上链,确保不可变性和信任。
随着消费者和政府对可持续采购的需求不断增加,这种扩展到供应链底层的可见性将有助于农食品公司跟踪和验证关键的可持续性指标。例如,农食品采购团队现在可以跟踪农民种植食品的情况、批准的化肥数量以及用于购买产品的水量,从而使他们能够与农民更密切地合作,确保可持续的实践。对于公司实现供应链的可持续性非常重要,因为麦肯锡的一份报告显示,80%的大型跨国公司对空气、土地、水、生物多样性和地质资源的影响不是来自内部运营,而是来自供应链,而大多数跨国公司在准确和高效评估供应商活动方面存在困难。
研究估计,全球农业供应链中有70%的小农户生活在每日3.20美元以下的全球贫困线之下,总计超过1.22亿人口。尽管小农户生产了全球三分之一的粮食,但他们仍面临贫困。
DiMuto农场管理应用程序还具有数字钱包功能,帮助农民跟踪、接收和使用数字付款。支付通道将帮助DiMuto执行小农户融资和保险计划,允许贷款和付款直接发放和到位接收。数字钱包还与DiMuto平台的贸易管理和种植功能相连接,为验证贷款的目的和使用,确保资金用于改善这些小农户的韧性和可持续性。
如果您对了解DiMuto如何帮助提高全球农食品贸易的可持续性感兴趣,请通过[email protected]与我们联系。
Sustainability can be simply defined as “meeting the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.” How can AgriFood companies of today achieve this seemingly loft vision?
Across industries, companies are now dedicated to regularly measuring their sustainability performance through sustainability reporting. According to KPMG’s biennial Survey of Sustainability Reporting 2022, a whopping 96% of the world’s 250 largest companies have reported their sustainability or ESG (environmental, social, and governance) matters.
Despite such high sustainability reporting rates, it’s difficult to determine if companies are becoming inherently more sustainable. This is especially alarming given the increase in global carbon emissions to record highs of 415.7 parts per million in 2021, which is 149% of pre-industrial levels. This is because of the complexity of global supply chains, especially more so for larger companies that often rely on partners, vendors and suppliers around the world to fulfil products and services, making it difficult to match reported metrics to what’s actually happening on the ground.
It is no wonder that scientists are still issuing looming warnings of the impending climate crisis, and time is too early to tell if the pivot to green investing and ESG investing yields actual positive impacts.
The FAO estimates that 31%, or 16.5 billion tonnes of carbon dioxide equivalents, of greenhouse gas emissions comes from the Agrifood supply chain. With the AgriFood industry being one of the key contributors to global emissions yet one of the least digitized industries, we need to make sure sustainability reporting, when adopted by AgriFood companies, results in actual positive sustainability changes.

Image: Person holding compost bin
How can DiMuto help?
DiMuto offers a farm-to-fork solution that captures critical data points with our solutions, that can eliminate data silos to form an accurate picture of sustainability levels. Our blockchain-powered solution helps to ensure immutability, showing the who, what and when of data inputs and creating foundation of trust.
We help to record:
- Farm Management Data
Such as fertilizer, water, electricity usage - Production Management Data
Such as raw materials used for packaging, utilities and more - Trade Management Data
Such as carbon footprint from sea shipments and air shipments - Inspection Management Data
Such as quality rejections, disposal levels and more
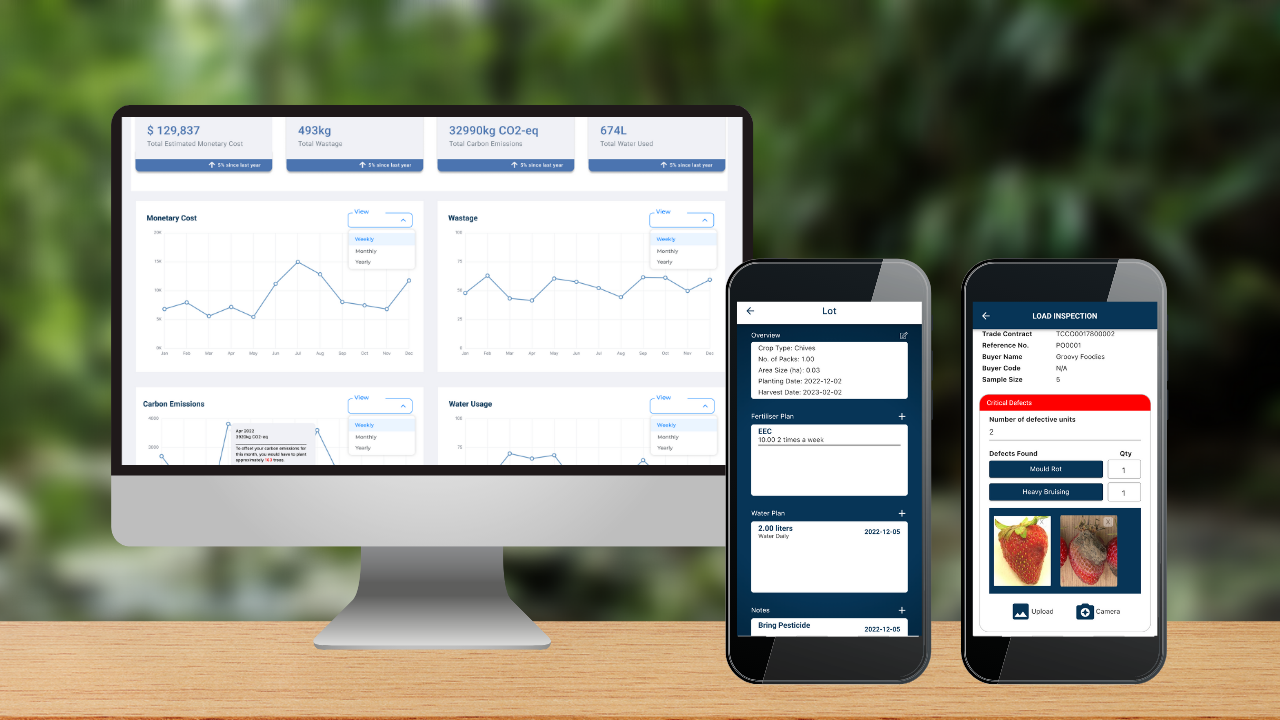
Image: L to R, DiMuto’s Sustainability Management Dashboard on Desktop, DiMuto’s Farm Management on Mobile Application, DiMuto’s Inspection Management on Mobile Application
For instance, the DiMuto Farm App records harvest and field data of smallholder farmers, connecting it to the packhouse production data and procurement data. This is especially important as 94% of agriculture workers are involved in the informal economy, according to the OECD.
Our solution also captures pre-shipment and post-shipment rejection data points to calculate real-time food waste level data, helping AgriFood companies to easily gain visibility on not just upstream but also downstream impacts, enabling more accurate Scope 1, 2 and 3

Image: Infographic of Scope 1, 2 and 3 Emissions
4 Key Metrics we help to measure and help AgriFood business owners to gain visibility on:
- Monetary Costs
Show opportunities to improve efficiency, sustainability, and long-term cost savings
- Food Waste
Highlight source of unnecessary greenhouse gas emissions and waste
- Carbon Emissions
Understand energy efficiency of their products’ carbon footprint
- Water Usage
See water footprint of their products and help ensure a resilient and safe water supply
These 4 key data types are then aggregated automatically on DiMuto’s Sustainability Management Dashboard. This dashboard helps Agrifood business owners to easily see the environmental impact of their operations and follow product lifecycles in real-time with useful metrics, which can be immediately generated into a report for it to be shared with relevant parties.

Image: Infographic of 4 Key Sustainability Metrics with statistics
AgriFood companies can now track and record accurate primary data, ensuring the reliability and efficiency of sustainability reporting of environmental metrics.
Capturing and analysing this data regularly and reliably empowers Agrifood business owners to identify opportunities for sustainable improvements, assess their progress, and determine new targets, helping to fuel a data-driven movement of food sustainability.
This is not to say that DiMuto is a magic bullet that can solve food sustainability, but working towards shedding light on real-live on the ground data through the supply chain, will help to build a more accurate picture on our sustainability progress, and allow us to work towards creating better standards of sustainability for the AgriFood industry.
If you are interested to learn more about how DiMuto helps improve sustainability of food systems for global AgriFood trade, reach us at [email protected].
人工智能(AI)在农食品产业中的应用近年来有着显著的增长。根据Markets&Markets的数据,农业行业在AI技术上的支出预计将从2020年的10亿美元增长到2026年的40亿美元。基于AI的解决方案具有巨大潜力,可以帮助农食品企业提高运营效率,做出更好的贸易决策,并更快地提供高质量的产品。鉴于这些优势,DiMuto已将AI技术融入我们的全球贸易解决方案,帮助客户实现更大的成功。
产品质量人工智能
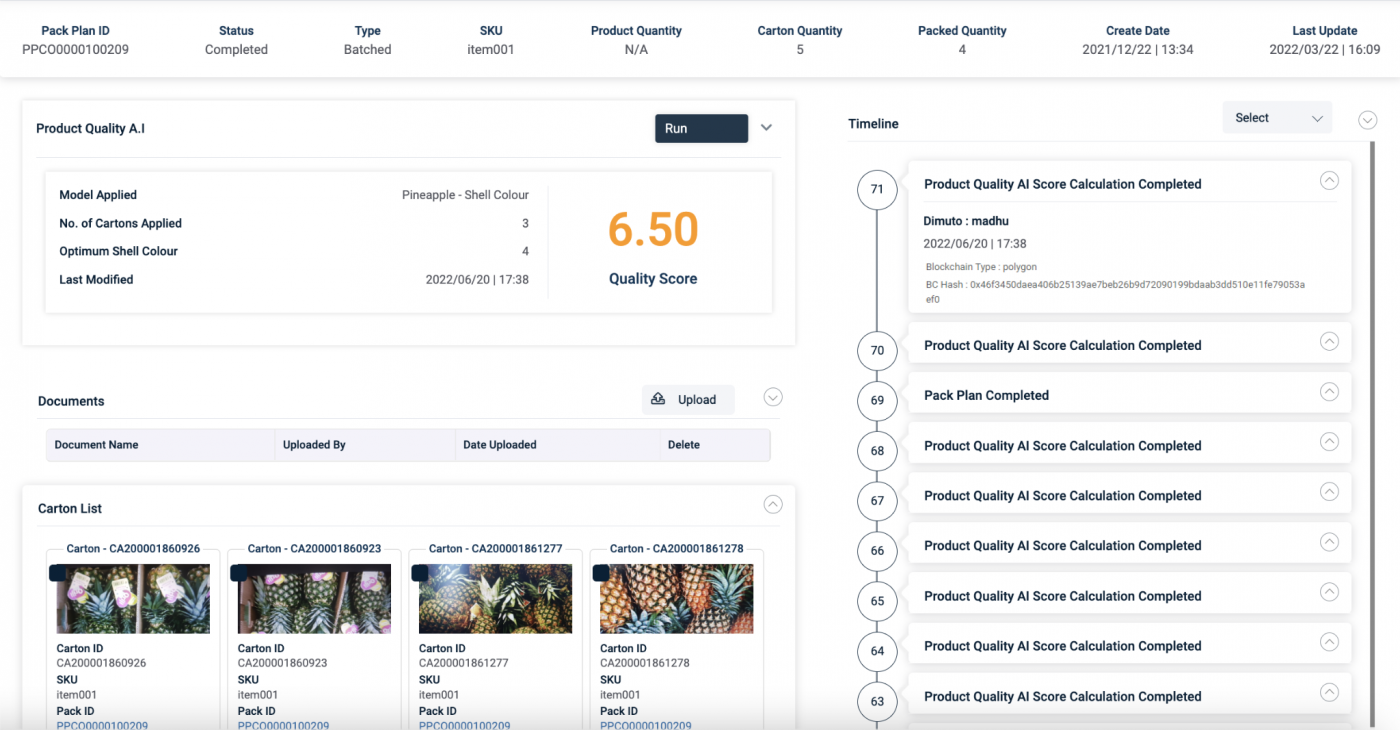
图片:DiMuto 平台上产品质量人工智能视图
首先,DiMuto开发了产品质量人工智能,帮助供应商向买家提供始终如一的高品质产品。农食品企业非常熟悉对其产品进行彻底的质量控制检查,以确定货物的质量和是否存在任何缺陷。然而,这一重要流程可能在企业运营中非常耗时,并且产品的质量可能因不同受众而有主观性。
借助人工智能,质量控制检查现在可以更高效、客观地进行。DiMuto的产品质量人工智能目前能够从三个关键方面分析水果产品:
1. 基于水果表面颜色检测成熟度
2. 基于长度和宽度确认水果大小
3. 检测每箱产品的数量
当用户将产品的图像捕捉并数字化到DiMuto系统时,这些人工智能分析可以即时生成在DiMuto平台上。此外,它还可以应用于使用DiMuto数字资产创建设备(DACKY)的移动传送线上。
贸易健康与融资人工智能
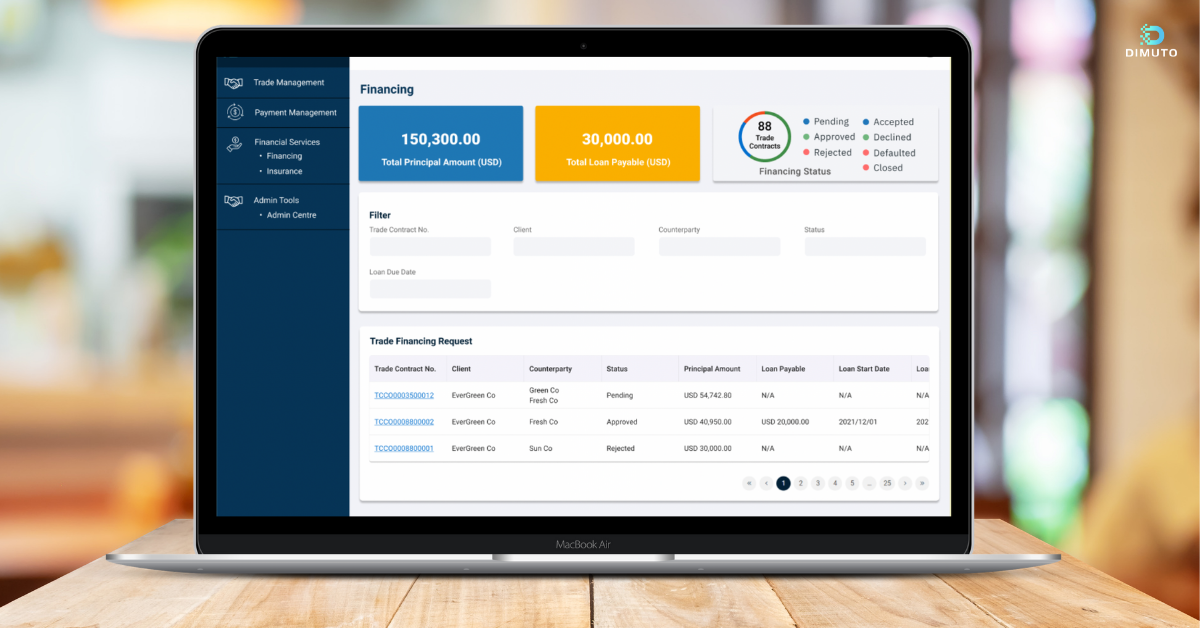
图片: DiMuto平台上贸易健康与融资人工智能首页视图
DiMuto金融服务利用人工智能来评估我们平台上每笔贸易交易的贸易健康和产品质量。在数字断裂且数据不透明的农食品产业中,处理易腐商品通常被金融机构视为充满风险。为了评估这种风险,银行和其他融资平台通常依赖于企业的历史财务文件。然而,评估这些文件可能不是一种可靠的方式来判断融资企业的风险,因为这些文件可能会被篡改、伪造或与当前业务无关。
DiMuto通过利用人工智能来避免这些问题,为农食品企业和金融机构提供以下服务:
1. 日常运营的可见性
2. 公司财务和运营实力的完整准确画像
3. 为金融机构提供低风险贷款机会,为买家/供应商提供商机
这些分析可以基于在DiMuto平台上捕获的每笔贸易的实时交易数据进行。结合产品质量人工智能,DiMuto可以为每笔交易和公司生成财务风险评分,以便用于发货后融资的机会。因此,DiMuto的贸易健康与融资人工智能使金融机构可以享受更深入的可见性和更可靠的保障,借款人可以获得更准确的风险评估和更灵活的条件。
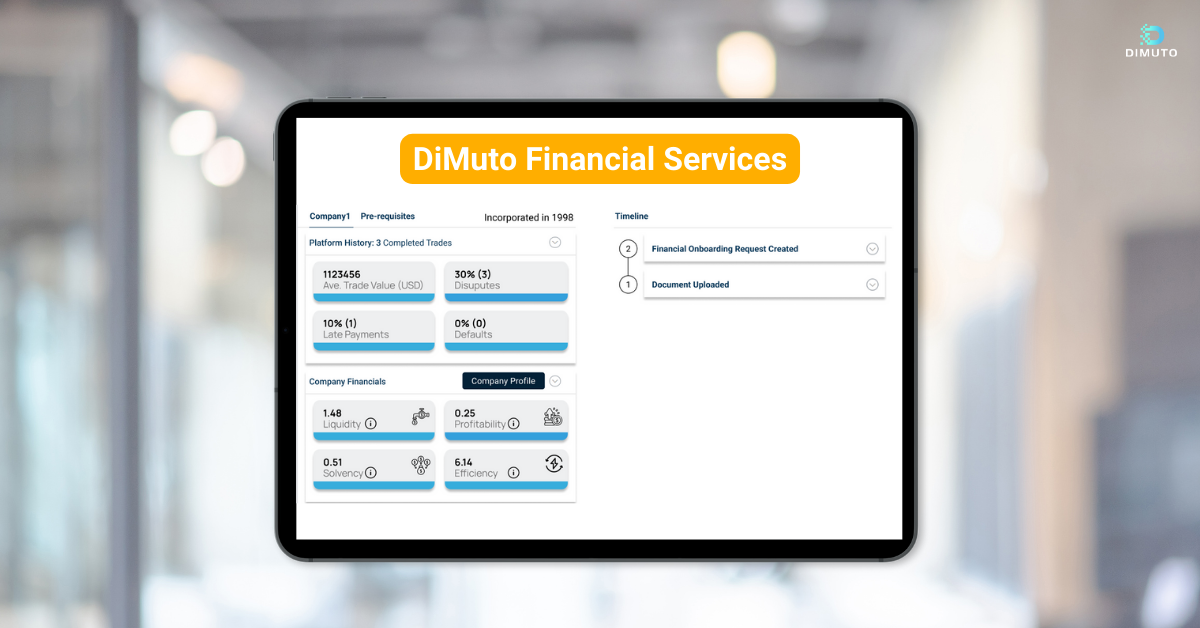
图片: DiMuto平台上贸易健康与融资人工智能屏幕视图
在DiMuto,我们深知人工智能对于赋能农食品企业做出更明智的贸易决策、提高运营效率、产品质量以及业务增长的重要性。通过与其他DiMuto功能的无缝集成,我们希望使人工智能技术对我们的客户来说更加易于接触和应用,以帮助促进更具韧性的全球农食品供应链的发展。

 English
English Español
Español

