In today’s world of rapidly advancing technology, the agrifood industry is facing a critical decision point. As the global population grows, the already complex and multifaceted agrifood supply chain is under increasing pressure. To ensure efficiency, transparency, and sustainability in this vital chain, digital transformation is no longer a luxury – it’s a necessity. Digitalization and automation have become increasingly ubiquitous as a way to increase productivity and improve efficient resource use, consistent with the need for a more sustainable food system.
Thus, digital transformation is crucial for the agrifood supply chain, as it enables visibility in the supply chain, forming the bedrock for the role of AI and data analytics to create a more sustainable future for food.
The Need for Digital Transformation in the Agrifood Supply Chain
The agrifood supply chain is a complex network that involves numerous stakeholders – from farmers and producers to distributors, retailers, and consumers. Traditionally, this chain has been managed using analog methods that are labor-intensive, time-consuming, and often fraught with inefficiencies. The lack of real-time information sharing and visibility across the entire supply chain results in problems such as overproduction, underutilized resources, food waste, and limited traceability. This is where digital transformation steps in.
From Analog to Digital: Breaking Down Data Silos with Digitization
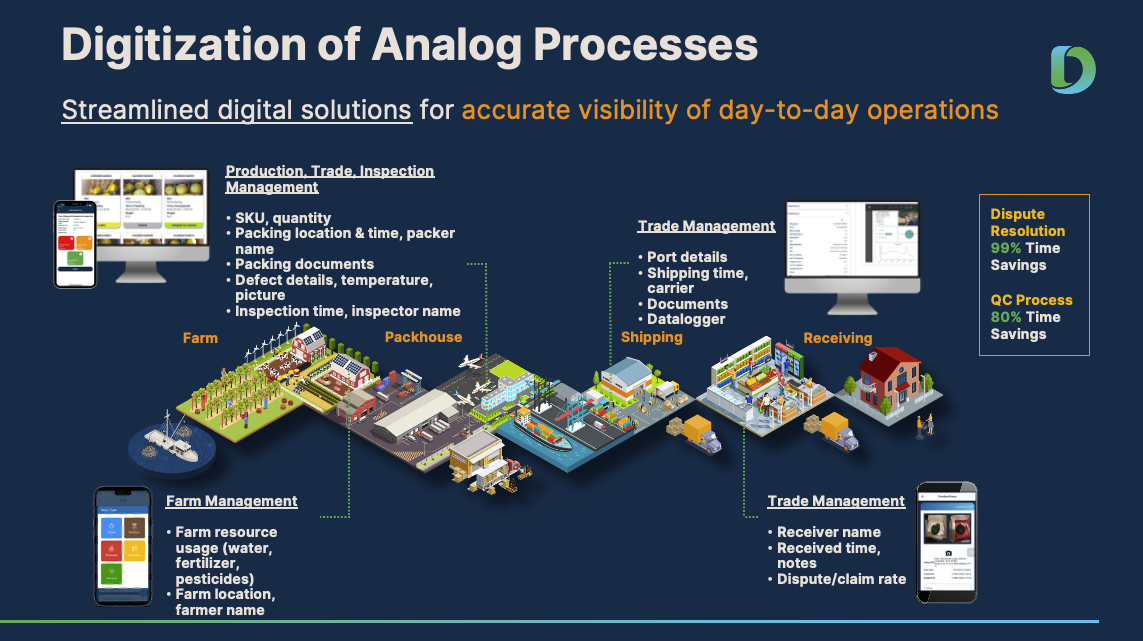
One of the primary challenges faced by the agrifood supply chain is the existence of data silos. Information is often trapped within individual stages of the chain, preventing seamless communication and collaboration.
What makes these data silos even more challenging to resolve is that much of this data exists in pen-and-paper format, even for large companies managing millions of dollars and thousands of products in their daily operations.
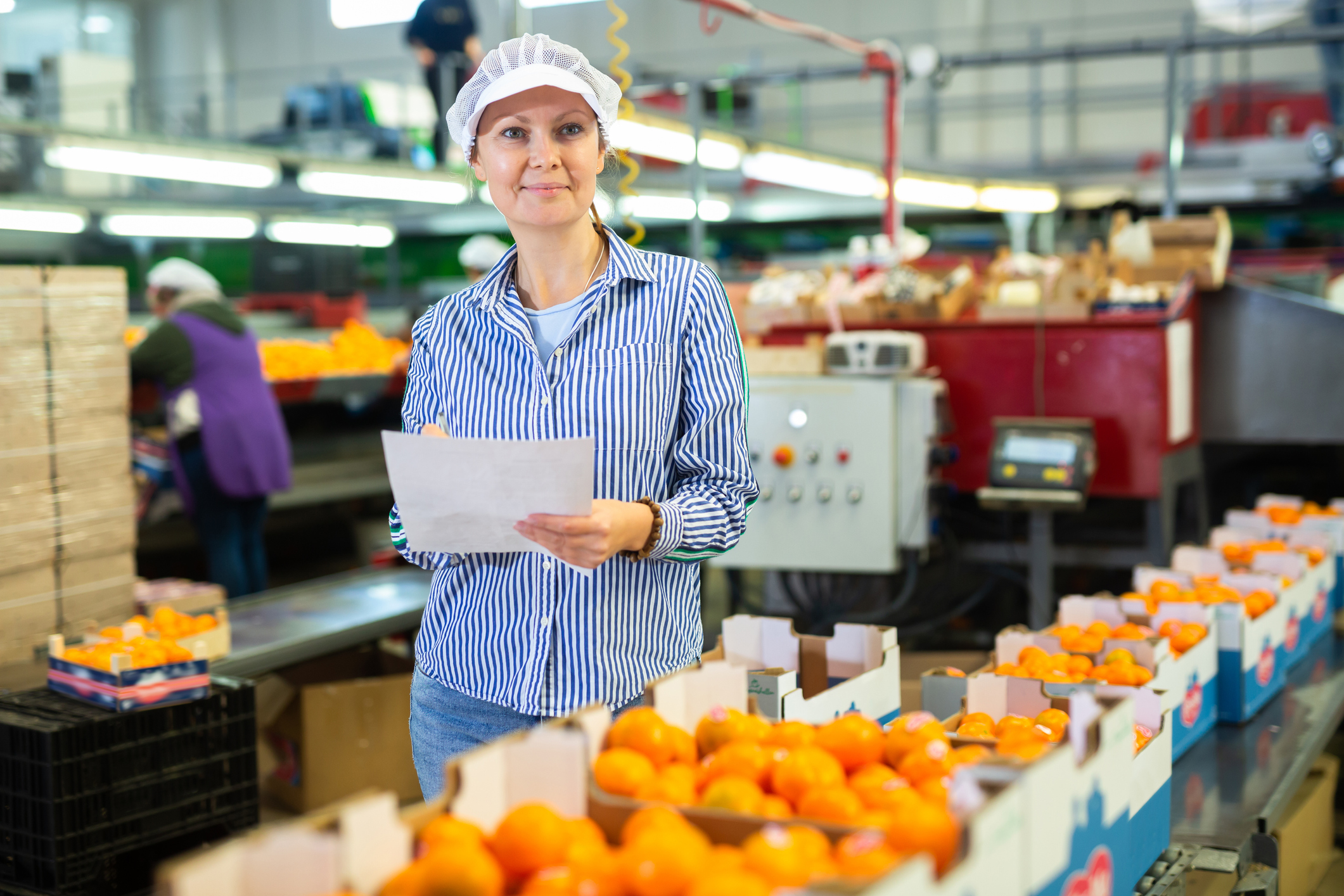

Above: Pen and paper are still being used to do quality check in many produce packinghouses today.
Additionally, companies often invest in additional manpower, time and resources to do additional sorting pre and post-shipment, just to reduce the possibility of facing rejections and quality issues further down the supply chain.
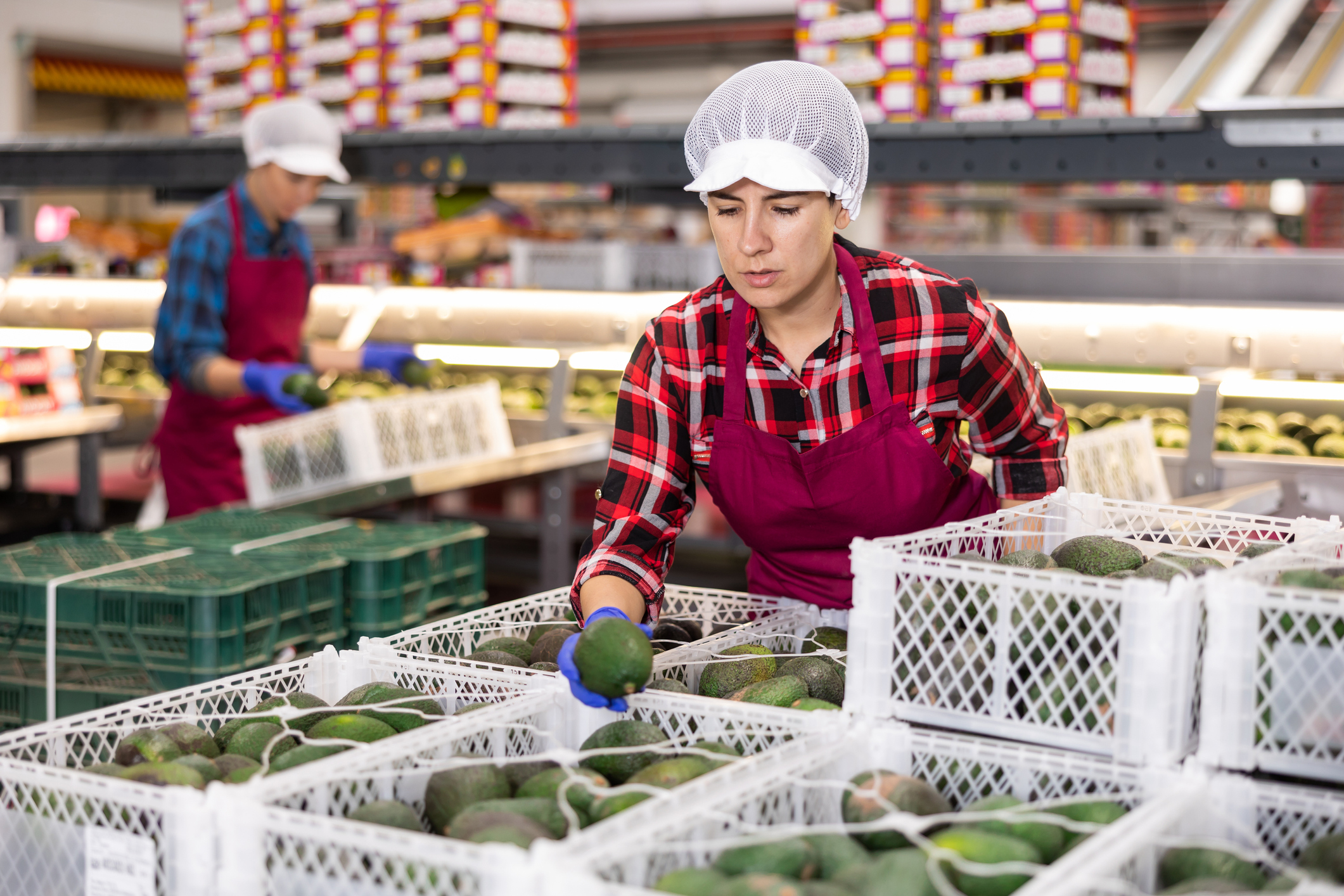

Above: Often, additional manpower is repeatedly deployed to check the quality of items such as fresh produce multiple times along the chain, often in a manual and time-consuming manner.
Thus, to have supply chain visibility, we must first digitize the analog to the digital, transforming operational processes in such a way that recording such data in the digital world is applicable, scalable and operational.
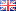
DiMuto’s QR code labels quickly creates a digital twin of each product and carton, allowing production and supply chain captured via our ecosystem of mobile app and web platform to be efficiently tagged to the digital twin of said product and carton.
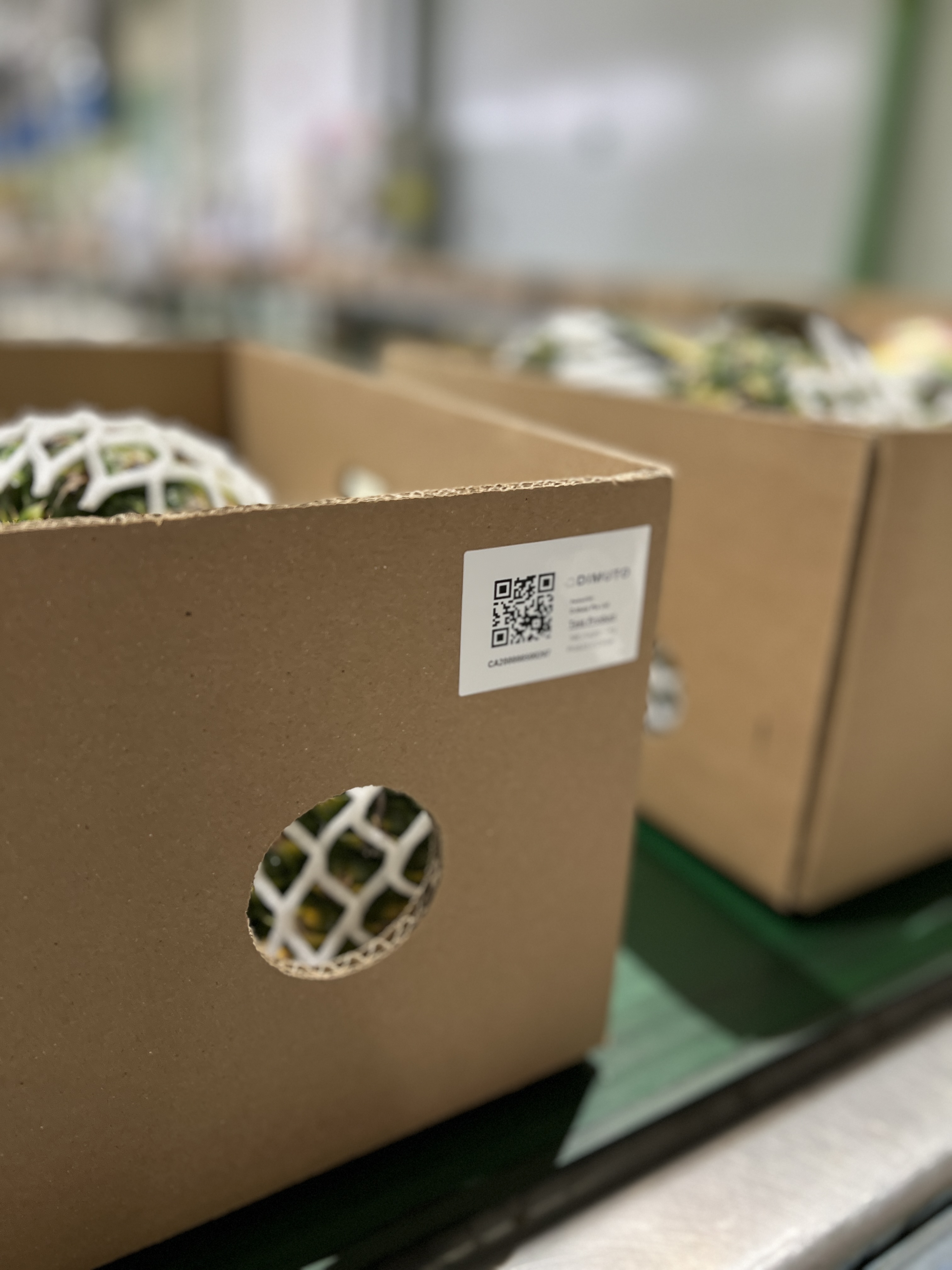

DiMuto’s QR Label can also be automatically integrated into existing barcode labels, eliminating duplicate labels, and printed on the spot for ease of use.
DiMuto’s Digital Transformation solution captures end to end data in one single platform. Read more here.
Enabling Supply Chain Visibility in One Platform
Supply chain visibility is the cornerstone of an effective and efficient agrifood supply chain. With digitization, stakeholders gain access to real-time data regarding the status of products, from farm to fork. Digital transformation involves the integration of technologies like IoT (Internet of Things) devices, sensors, and blockchain to gather and share data across all stages of the supply chain. This real-time data sharing not only enhances visibility but also enables quick decision-making, reduces waste, and improves overall efficiency.
However, even when data is digital and processes are digitalized, another challenge is that there is currently no one solution that can do it all in the market. There are a multitude of specialized software tackling one part of the supply chain or specific activities, and no one software solution that can connect all the dots. DiMuto is designed specifically to solve this, providing the different stakeholders the option of manually uploading, or integrating with the different existing solutions in use by supply chain players. This helps create a complete picture of the supply chain data, creating true supply chain visibility.
Benefits for Agrifood Businesses
For agrifood businesses, the benefits of embracing digital transformation are far-reaching. The newfound supply chain visibility provided by digitization allows for proactive decision-making and improved resource allocation. Growers can fine-tune their planting and harvesting schedules based on real-time data, minimizing the risk of crop losses due to unforeseen weather events or disease outbreaks. Traders, Importers, and Exporters can streamline their operations by having precise knowledge of incoming shipments, enabling better production planning and reducing waste. Retailers can optimize inventory management, preventing stockouts and reducing excess inventory costs. Moreover, the ability to provide consumers with detailed information about the journey of their food enhances brand reputation and consumer loyalty. Ultimately, agrifood businesses that embrace digital transformation position themselves as leaders in sustainability, efficiency, and innovation, driving growth and success in an increasingly competitive market.
The Role of AI and Data Analytics
As data flows freely through the digitized agrifood supply chain, AI and data analytics step in to make sense of the massive datasets generated. AI algorithms can predict crop yields, optimize transportation routes, and even foresee potential disruptions. Advanced analytics provide insights into consumer preferences, helping farmers tailor their production to meet market demands. Additionally, AI-powered demand forecasting minimizes food waste by ensuring that the right amount of produce is grown and distributed.
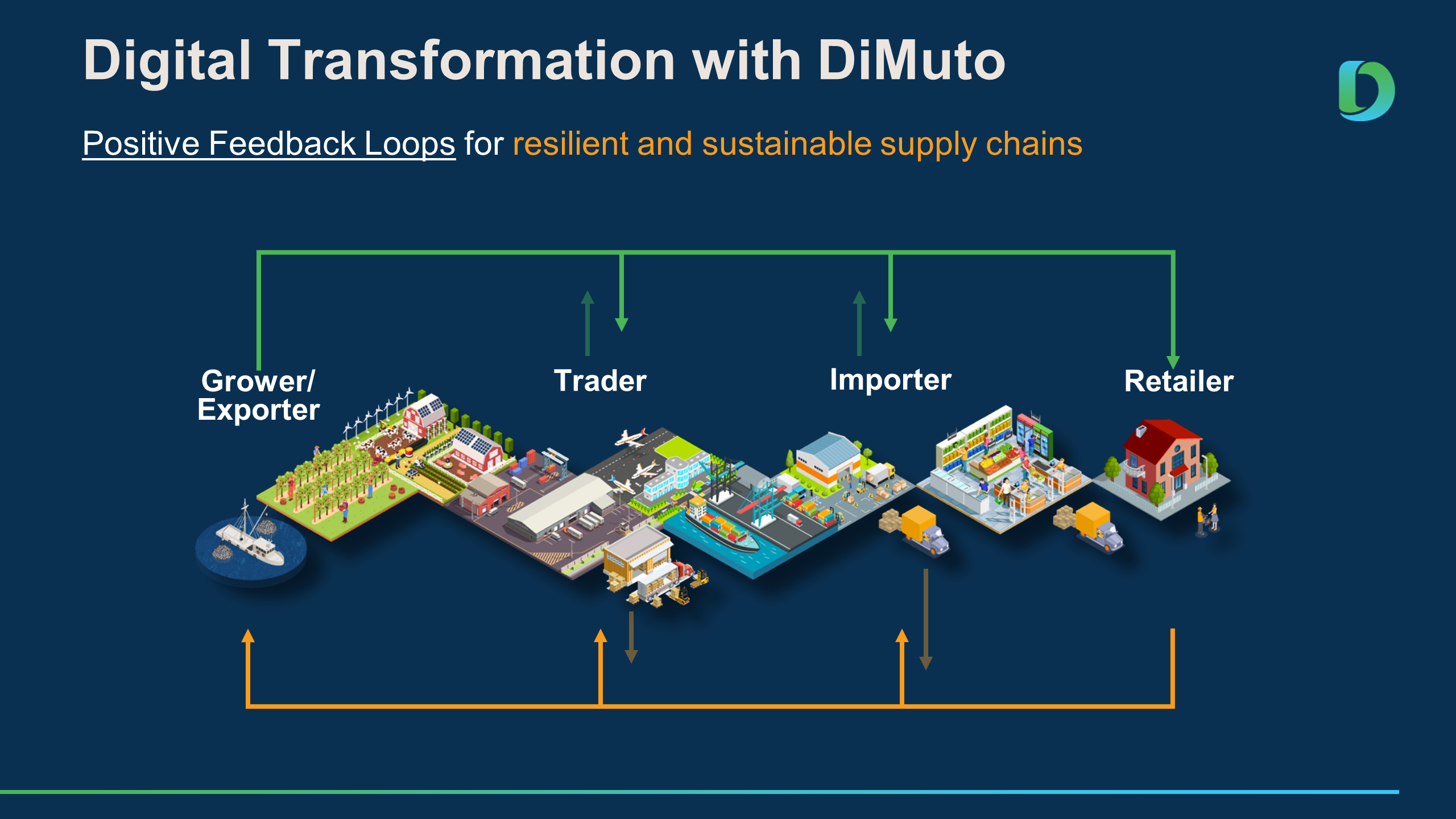
Creating a digitally transformed food supply chain allows for positive feedback loops where Data Analytics and AI can be applied for sustainability and efficiency
Paving the Way for Sustainable Food Systems
A significant motivation for embracing digital transformation in the agrifood sector is the pursuit of sustainability. With accurate data and insights, stakeholders can adopt precision agriculture practices that minimize the use of resources like water, pesticides, and fertilizers. By preventing overproduction and enhancing distribution efficiency, digital technologies play a crucial role in reducing food waste. Ultimately, a more sustainable food system emerges, contributing to environmental conservation and social responsibility.
The agrifood supply chain urgently needs to transition from analog to digital solutions to enhance visibility, efficiency, and sustainability. Breaking down data silos and adopting technologies like IoT, sensors, and blockchain gives real-time insights to empower stakeholders to make informed decisions. AI and data analytics optimize the system’s efficiency to meet the challenges of a growing global population and increasing environmental concerns.
A Need For Digital Transformation Of Agrifood Supply Chain
In the face of a growing global population and the intricacies of the agrifood supply chain, digital transformation has become a necessity rather than a luxury. The shift from traditional methods to digitalization and automation is vital to enhance efficiency, transparency, and sustainability. By digitizing operations and breaking down data silos, real-time communication and collaboration among stakeholders can be achieved. QR code labels and digital twins, exemplified by DiMuto, facilitate supply chain visibility and data capture from production to distribution. Incorporating technologies like IoT, sensors, and blockchain enables informed decision-making, waste reduction, and increased efficiency. AI and data analytics further contribute by predicting yields, optimizing routes, and tailoring production. Sustainability is a driving force behind this transformation, allowing resource conservation and waste reduction, ultimately leading to a more sustainable food system with environmental and social benefits.
Find out more in this article