Cross-border Transactions Today
In 2020, the market growth for international payments reached an all-time high with forecasted revenues of $2Trillion USD, according to a recent forecast by Smarter Payments Tracker. However, research has shown that only 1% of small and medium enterprises (SMEs) use digital finance successfully, even though SMEs represent and more than 50% of employment worldwide.
Add that to the complex regulations and infrastructure of cross-border payment systems today, it is no wonder that moving money across borders is still far from an efficient and easy process. This problem will only become more pertinent as the role of SMEs in the global economy continues to grow. Challenges faced when conducting cross-border payments include:
- Country-specific regulations
- Slow processing of transactions
- Expensive costs
- Security concerns
- Lack of visibility
Country-specific rules have impeded international payments, and transactions routed through intermediate institutions can take days to complete and typically come with costs. Due to the numerous intermediaries involved in transferring money from one nation to another, all of which collect fees for their services, cross-border payments are notoriously expensive. Regulatory costs pile up, and FX fees for converting one currency to another will be levied. Compounding this is the lack of clarity when it comes to remittance fee structures.
Additionally, unlike near-instantaneous domestic payments, traditional cross-border bank transfers typically involve numerous exchanges of hands in one transaction and take two to five days to process, making it difficult to expect payments on time.
On top of that, high-level security breaches in cross-border payment systems are common, as evidenced by the $81 Million theft on Bangladesh’s central bank in 2016. As each country has its own set of rules, the cross-border payment system is vulnerable to hacking whenever funds enter a country with lax security and access policies.
As each country has its own set of rules, the cross-border payment system is vulnerable to hacking whenever funds enter a country with lax security and access policies.
Another core concern of businesses making cross-border payments is the lack of visibility of payment status. according to a poll conducted by SWIFT and EuroFinance in 2017, 64 percent of businesses desire real-time payment tracking capabilities, while 47 percent want improved insight into the costs and deductions involved.
With the longstanding lack of real-time tracking of payment status, businesses often do not have certainty of transaction status. When companies need to know the current status of a payment, they are dependent on operations specialists undertaking manual research to ascertain basic information. Payment inquiries must be directed through correspondent banks, then communicated back to clients to determine any necessary actions. This lack of transparency creates a high informational cost, undermines corporate cash flow forecasts, and can strain relationships with a client’s suppliers and busines partners when funds are not received as expected.
For AgriFood companies with a significant portion of business in export-import trade, the ability to conduct and manage payment transactions across borders in an efficient, secure and visible manner is a concern. The risks of cross-border payments today are especially great for AgriFood companies dealing with a high volume of international trade transactions where one container of fresh produce can easily amount to an average cost of USD$50,000 to 150,000.
A need for trade-centric payment management in global AgriFood Trade
In global AgriFood Trade, there’s not only a need for cross-border payment methods to have less friction but have a trade-centric perspective as well. This is because product movement is dependent on a multitude of factors and delays and changes in timelines are commonplace. Trade disputes involving quality issues are typical and can cause upwards of 5-15% of trade value.

Trade Dispute Due to Poor Product Quality of Oranges, read more.
Thus, it is particularly important for finance teams to be informed of situations affecting expected payments and cash flow.
DiMuto Unifies Products, Documents and Payments in One
DiMuto connects products, documents and payments on a single platform, giving visibility across departments and functions in a company. We digitalize physical AgriFood products by tagging each fruit or vegetable with a Digital Identity Label (DID).

DiMuto’s DIDs Tagged onto Cartons of Bananas to Provide Visibility Across All Departments, read more.
DIDs act as a digital identifier for each fruit and contain product quality and traceability data and allow companies to connect the product to digital documents and payments on DiMuto Platform.
DiMuto Payment Management
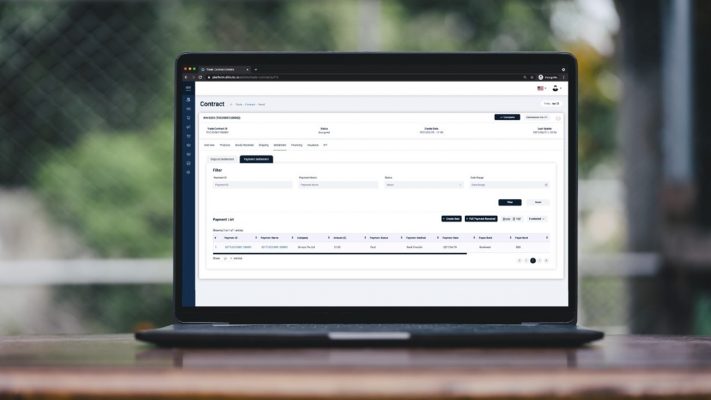
DiMuto allows payment receipts to be uploaded onto the blockchain automatically, ensuring immutability. Payment status is also viewed in the same trade timeline as other trade actions, ensuring that both sales and finance understand the trade situation. The DiMuto Payment Management feature also allows companies to conduct cross-border transactions via the DiMuto Platform.
DiMuto Payment Powered by OPAL
A partner that we work with to make this possible is OPAL Payments, a Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS)-licensed Major Payment Institution (MPI), which provide businesses with a less expensive and more convenient method of international payment and cross-border banking through Global Digital Business Accounts.
Through this partnership, companies on the DiMuto Platform will be able to receive payments rapidly in important markets such as the United States, the United Kingdom, the European Union, and more, as well as access local payment networks in 21 countries without the need to set up business operations in these territories. OPAL understands that SMEs encounter challenges when it comes to transacting business on a global basis.
Beyond connecting payments in traditional currencies, the DiMuto Payment Management can allow transactions in the USD Coin (USDC), through CIRCLE, a uniform platform for businesses to collect payments and send payouts around the world using blockchain technology. Meeting the needs of high-volume trading firms, crypto exchanges, and market makers, the USD Coin (USDC) is a significant advancement in the way businesses utilize money. Digital dollars function similarly to other digital content: they travel at the speed of the internet, can be traded in the same manner that we share content, and are less expensive and more secure than current payment systems.
A Bright Future: Paving the way to trade financing access
By digitalizing physical AgriFood assets, asset tracking is now possible – the identity, movement and condition of individual products and cartons can now be easily tracked and traced with DiMuto. Coupled with Artificial Intelligence Models that can objectively assess product quality and trade health, DiMuto helps lower the risk associated with trade financing for agri-perishables, giving AgriFood SMEs opportunities to obtain much needed trade financing options.
The US$1.9 trillion global trade finance gap has deteriorated as a result of Covid-19, which is now projected to be as high as US$3.4 trillion by experts, with SMEs in emerging nations being the hardest hurt. Due to concerns such as creditworthiness, collateral requirements, short-term liquidity, and political or currency risk, SMEs have historically had difficulty obtaining institutional funding.
More efficient and trade-centric cross-border payment methods will not only create more visibility and help business manage their operations and cash flow better but also help to provide them with trade financing opportunities to help their businesses grow greater.
If you are interested to learn more about how DiMuto helps Agri-Food businesses with cross-border payment management, please reach us here or drop us an email at sales@dimuto.io.